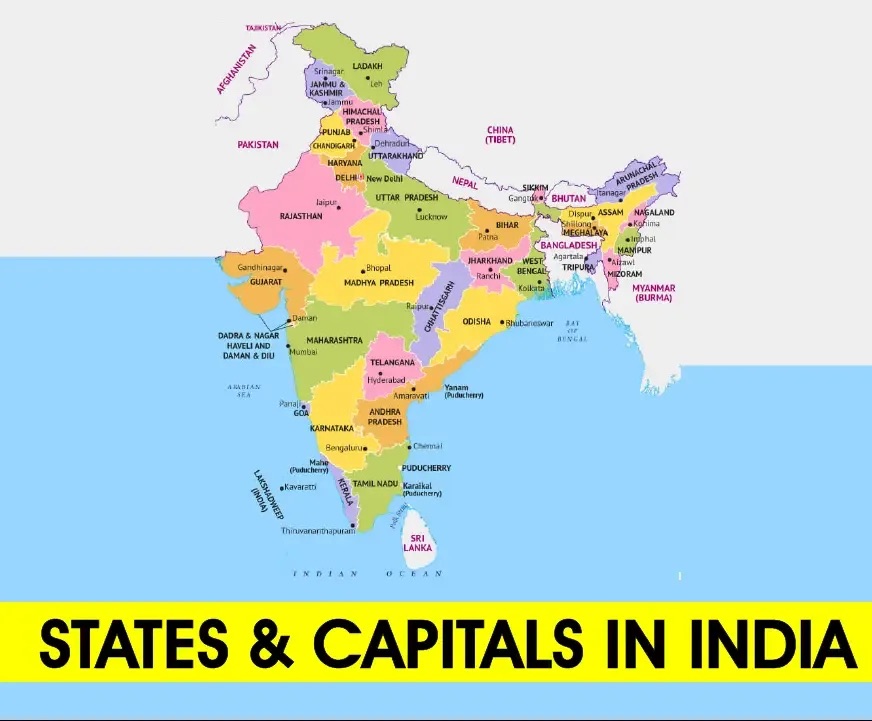
States and Capitals of India has a total of 28 States and 8 Union Territories, each with its own distinct and diverse culture, language, resources, flora and fauna, democratic festivals, and more. Every state plays a role in the country’s economic development and growth in various ways.
States and Capitals of India
India is the 7th largest country in the world by area, divided into various states and union territories, each contributing uniquely to the country’s identity. This article delves into the States and Capitals of India, including those established post-independence. A significant reorganization took place in 1956 based on language, resulting in the creation of new states and capitals. Additionally, Union Territories and their capitals in India are explored in this discussion.
List of States and Capitals of India
India comprises 28 states and 8 union territories. Below is the comprehensive list of 28 States and Capitals of India:
|
Sl.No.
|
States
|
Capital
|
|
1.
|
Andhra Pradesh
|
Amaravati
|
|
2.
|
Arunachal Pradesh
|
Itanagar
|
|
3.
|
Assam
|
Dispur
|
|
4.
|
Bihar
|
Patna
|
|
5.
|
Chhattisgarh
|
Raipur
|
|
6.
|
Goa
|
Panaji
|
|
7.
|
Gujarat
|
Gandhinagar
|
|
8.
|
Haryana
|
Chandigarh
|
|
9.
|
Himachal Pradesh
|
Shimla
|
|
10.
|
Jharkhand
|
Ranchi
|
|
11.
|
Karnataka
|
Bangalore
|
|
12.
|
Kerala
|
Thiruvananthapuram
|
|
13.
|
Madhya Pradesh
|
Bhopal
|
|
14.
|
Maharashtra
|
Mumbai
|
|
15.
|
Manipur
|
Imphal
|
|
16.
|
Meghalaya
|
Shillong
|
|
17.
|
Mizoram
|
Aizawl
|
|
18.
|
Nagaland
|
Kohima
|
|
19.
|
Odisha
|
Bhubaneshwar
|
|
20.
|
Punjab
|
Chandigarh
|
|
21.
|
Rajasthan
|
Jaipur
|
|
22.
|
Sikkim
|
Gangtok
|
|
23.
|
Tamil Nadu
|
Chennai
|
|
24.
|
Telangana
|
Hyderabad
|
|
25.
|
Tripura
|
Agartala
|
|
26.
|
Uttarakhand
|
Dehradun
|
|
27.
|
Uttar Pradesh
|
Lucknow
|
|
28.
|
West Bengal
|
Kolkata
|
List of Union Territories of India
|
Sl. No.
|
Union Territories
|
Capital
|
|
1.
|
Ladakh
|
Leh
|
|
2.
|
Jammu and Kashmir
|
Srinagar- Summer Capital
Jammu- Winter Capital
|
|
3.
|
Puducherry
|
Puducherry
|
|
4.
|
Lakshadweep
|
Kavaratti
|
|
5.
|
Andaman and Nicobar Islands
|
Port Blair
|
|
6.
|
Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu
|
Daman
|
|
7.
|
Chandigarh
|
Chandigarh
|
|
8.
|
The Government of NCT of Delhi
|
Delhi
|
List of States formed after 1947 in Independent India
|
State
|
Year Formed
|
Details
|
|
Jammu and Kashmir
|
1948
|
Merged into the Indian Union after signing the Instrument of Accession; Ladakh and Jammu and Kashmir became separate union territories in 2019.
|
|
Uttar Pradesh
|
1950
|
Formerly known as United Province, it was reorganized and renamed Uttar Pradesh in 1950.
|
|
Bihar
|
1950
|
Formed as a full state on 26 January 1950; Jharkhand was later carved out from Bihar in 2000.
|
|
Assam
|
1950
|
Gained state status on 26 January 1950; reorganized from a British province to a full state.
|
|
Orissa (Odisha)
|
1950
|
Made a separate province on 1 April 1936 and became a state on 26 January 1950; renamed Odisha in 2011.
|
|
Tamil Nadu
|
1950
|
Formerly Madras Presidency; reorganized as a state in 1950 and renamed Tamil Nadu in 1969.
|
|
Andhra Pradesh
|
1956
|
Formerly part of Madras State; became a separate state on 1 November 1956; Telangana was carved out of it in 2014.
|
|
Madhya Pradesh
|
1956
|
Formed on 1 November 1956; Chhattisgarh was separated from it in 2000.
|
|
Kerala
|
1956
|
Merged former states of Travancore, Cochin, and Malabar to form Kerala on 1 November 1956.
|
|
Karnataka
|
1956
|
Originally Mysore State; renamed Karnataka in 1973; formed on 1 November 1956.
|
|
Maharashtra
|
1960
|
Formed along with Gujarat from Bombay Province on 1 May 1960.
|
|
Gujarat
|
1960
|
Separated from Bombay Presidency and formed as an independent state on 1 May 1960.
|
|
Nagaland
|
1963
|
Became a state on 1 December 1963, separated from Assam.
|
|
Punjab
|
1966
|
Formed after the merger of Patiala and other princely states; Haryana was separated from it in 1966.
|
|
Himachal Pradesh
|
1971
|
Formed on 25 January 1971; initially a union territory, it gained statehood later.
|
|
Manipur
|
1972
|
Became a state on 21 January 1972 after being a union territory since 1956.
|
|
Meghalaya
|
1972
|
Originally an autonomous state within Assam; became a separate state on 21 January 1972.
|
|
Tripura
|
1972
|
Transitioned from a union territory to a state on 21 January 1972.
|
|
Sikkim
|
1975
|
Merged with the Indian Union on 16 May 1975, becoming a full state.
|
|
Goa
|
1987
|
Liberated from Portuguese rule in 1961, became a union territory; formed as a state on 30 May 1987.
|
|
Arunachal Pradesh
|
1987
|
Initially a union territory in 1972, became a state in 1987.
|
|
Mizoram
|
1987
|
Declared a full state on 20 February 1987, after being a district of Assam and later a union territory.
|
|
Chhattisgarh
|
2000
|
Separated from Madhya Pradesh on 1 November 2000.
|
|
Jharkhand
|
2000
|
Formed from Bihar on 15 November 2000.
|
|
Uttarakhand
|
2000
|
Initially named Uttaranchal; formed from districts of Uttar Pradesh; renamed Uttarakhand in 2007.
|
|
Telangana
|
2014
|
Formed on 2 June 2014 from the north-western part of Andhra Pradesh.
|
States of India: 28 States Important Points
Below is a concise summary of the various states in India:
Andhra Pradesh
- Andhra Pradesh is situated on the southeast coast of India. It is the seventh-largest state in India by area, spanning 162,975 square kilometers, and the tenth most populous state with a population of 49,386,799 people.
- Telangana borders it to the northwest, Chhattisgarh to the north, Tamil Nadu to the south, Karnataka to the west, and the Bay of Bengal to the east.
- Andhra Pradesh is the first state to be formed on a linguistic basis in India on 1 October 1953.
- Telugu is the official language spoken and is recognized as the “rice bowl of India”.
Capital: Hyderabad Founded on: 1 Nov. 1956 Official Language: Telugu
Arunachal Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh shares its borders with Assam and Nagaland. It shares international borders with Bhutan, Myanmar, and China.
- Arunachal Pradesh is home to 26 major tribes of India and about 100 sub-tribes.
- In 2011, Arunachal Pradesh had a population of 1,382,611 residing in an area of 83,743 square kilometers.
- Arunachal Pradesh was formed from the North-East Frontier Agency area and is the biggest state among the Seven Sister States.
Capital: Itanagar Founded on: 20 Feb. 1987 Official Language: English
Assam
- Assam covers an area of 78,438 square kilometers and shares a border with Bhutan, Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur, Meghalaya, Tripura, Mizoram, Bangladesh, and West Bengal.
- Dispur is the capital and Assamese is the official language.
- The first place where oil drilling took place in Asia was Assam.
- The economy and society of Assam are dependent on the wildlife tourism of Kaziranga and Manas National Parks. These two wildlife parks are World Heritage Sites.
Capital: Dispur Founded on: 26 Jan. 1950 Official Language: Assamese
Bihar
- Bihar is the 12th largest state by territory, with an area of 94,163 kilometers square, and shares borders with Uttar Pradesh, Nepal, West Bengal, and Jharkhand.
- The plains of Bihar are split by the river Ganga, which flows from west to east.
- Bihar is the world’s fourth-most populous state and the common languages spoken are Hindi, Urdu, Maithili, Magahi, Bhojpuri, etc.
Capital: Patna Founded on: 26 Jan. 1950 Official Language: Hindi
Chhattisgarh
- Chhattisgarh is the 9th-largest state in India, with an area of 135,192 km2.
- As of 2020, it has a population of roughly 29.4 million, making it the 17th most populated state in the country.
- The state was formed by the partition of ten Chhattisgarhi and six Gondi-speaking districts in the southeast of Madhya Pradesh. Its capital city is Raipur.
- It shares its borders with Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Jharkhand, Odisha, Telangana, and Andhra Pradesh. Currently, it comprises 28 districts.
Capital: Raipur Founded on: 1 Nov. 2000 Official Language: Hindi
Goa
- Goa is surrounded by the Indian states of Maharashtra to the north and Karnataka to the east and south, with the Arabian Sea forming its western coast.
- It is India’s smallest state by area and its fourth-smallest by population.
- Goa has the highest GDP per capita among all Indian states and it is the third-highest ranking among Indian states in the human development index.
- Until it was annexed by India in 1961 Goa was the overseas territory of the Portuguese Empire. Goa’s official language, which is spoken by a majority of its inhabitants, is Konkani.
Capital: Panaji Founded on: 30 May. 1987 Official Language: Konkani, English
Gujarat
- Gujarat is a state on the western coast of India with a coastline of 1,600 km, and it is the state of India having the longest coastline and a population of 60.4 million.
- It is the fifth-largest Indian state by area and the ninth-largest state by population.
- The capital city of Gujarat is Gandhinagar, while its largest city is Ahmedabad. The Gujarati people of India are indigenous to the state, and their language Gujarati is the state’s official language.
Capital: Gandhinagar Founded on: 1 May. 1960 Official Language: Gujarati
Haryana
- Haryana has an area of 44,212 km2 and it is ranked 20th in terms of area, with less than 1.4% of India’s land area.
- Chandigarh is the state capital, and Faridabad in National Capital Region (NCR) is the most populous city of the state.
- Gurgaon is considered one of the major information technology and automobile hubs of India.
Capital: Chandigarh Founded on: 1 Nov. 1966 Official Language: Hindi
Himachal Pradesh
- Haryana shares a border with Jammu and Kashmir, Ladakh, Punjab, Haryana, Uttarakhand, and a very narrow border shared with Uttar Pradesh to the South.
- The state also shares an international border with the Tibet Autonomous Region in China.
- In 1966, hilly areas of neighboring Punjab state were merged into Himachal and it was ultimately granted full statehood in 1971.
- Nearly, 90% of the state’s population lives in rural areas. The important constituents of the state’s economy are agriculture, horticulture, hydropower, and tourism.
Capital: Shimla Founded on: 25 Jan. 1971 Official Language: Hindi
Mizoram
- Mizoram shared borders with three of the Seven Sister States Tripura, Assam, and Manipur.
- The state also shares a 722-kilometer border with the neighboring countries of Bangladesh and Myanmar.
- Like several other northeastern states of India, Mizoram was previously part of Assam until 1972.
Capital: Aizawl Founded on: 20 Feb. 1987 Official Language: Mizo
Jharkhand
- Jharkhand is a state in eastern India and it shares its border with the states of Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, and West Bengal.
- It has an area of 79,710 km2 which is the 15th largest state by area and the 14th largest by population. Hindi is the official language of the state.
- The city of Ranchi is its capital and Dumka is its sub-capital.
Capital: Ranchi Founded on: 15 Nov. 2000 Official Language: Hindi
Karnataka
- According to the size, Karnataka is the largest state in South India and the sixth-largest in India.
- The state is in the southwestern region of India. Its capital and largest city is Bangalore and it shares bordered by the Arabian Sea to the west, Goa, Maharashtra, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, and Kerala.
- It is the only southern state to have land borders with all of the other 4 southern Indian sister states.
Capital: Bangalore Founded on: 1 Nov. 1956 Official Language: Kannada
Kerala
- Kerala is a state on the Malabar Coast of India. Spread over 38,863 km2.
- It is bordered by Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, and the Lakshadweep Sea.
- As per the 2011 Census, there is a 33,406,061 Population of people and it is the thirteenth-largest Indian state by population.
Capital: Thiruvananthapuram Founded on: 1 Nov. 1956 Official Language: Malayalam
Madhya Pradesh
- Madhya Pradesh is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal, and Madhya Pradesh is the second-largest Indian state by area and the fifth-largest state by population with over 72 million residents.
- It borders the states of Uttar Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Maharashtra, Gujarat, and Rajasthan.
- The economy of Madhya Pradesh is the 10th-largest in India and has the country’s 26th-highest per-capita income.
Capital: Bhopal Founded on: 1 Nov. 1956 Official Language: Hindi
Maharashtra
- Maharashtra is divided into 6 divisions and 36 districts, with the state capital being Mumbai, also the most populous urban area in India, and Nagpur serving as the winter capital.
- The Godavari and the Krishna are the two major rivers in the state. Nearly 60% of cultivable land in Maharashtra is producing Jowar.
- Spread over 307,713 km2, it is the third-largest state by area in India. Pune and Nashik are known as the ‘Oxford of the East’ and the ‘Wine Capital of India’ respectively.
Capital: Mumbai Founded on: 1 May. 1960 Official Language: Marathi
Manipur
- Manipur is bounded by the Indian states of Nagaland, Mizoram, and Assam.
- The state covers an area of 22,327 square kilometers and has a population of almost 3 million.
- According to the 2011 census, Hinduism is the major religion in the state, followed by Christianity.
Capital: Imphal Founded on: 21 Jan. 1972 Official Language: Manipuri
Meghalaya
- On 21 January 1972, Meghalaya was formed by carving out two districts from the state of Assam Hills.
- The population of Meghalaya as of 2016 is estimated to be 3,211,474. Meghalaya covers an area of approximately 22,430 square kilometers.
- The state is bound to the south and west by Bangladesh, and to the north and east by Assam.
Capital: Shillong Founded on: 21 Jan. 1972 Official Language: English
Nagaland
- Nagaland is bordered by the state of Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, and Myanmar.
- Nagaland’s capital city is Kohima and its largest city is Dimapur.
- It has an area of 16,579 square kilometers with a population of 1,980,602 per the 2011 Census of India, making it one of the smallest states of India.
Capital: Kohima Founded on: 1 Dec. 1963 Official Language: English
Odisha
- Odisha is the 8th largest state by area and the 11th largest by population. The state has the third-largest population of Scheduled Tribes in India.
- It shares borders with West Bengal, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Andhra Pradesh, and Telangana. Odisha has a coastline of 485 kilometers along the Bay of Bengal.
- The capital of Odisha is Bhubaneswar. The economy of Odisha is the 16th-largest state economy in India with ₹5.33 lakh crore and Odisha ranks 32nd among Indian states in the human development index.
Capital: Bhubaneswar Founded on: 26 Jan. 1950 Official Language: Odia
Punjab
- Punjab covers an area of 50,362 square kilometers which is only 1.53% of India’s total geographical area.
- It is the 20th-largest Indian state by area. With over 27 million inhabitants, Punjab is the 16th-largest state by population, comprising 23 districts.
- The state capital is Chandigarh, a Union Territory and also the capital of the neighboring state of Haryana.
Capital: Chandigarh Founded on: 1 Nov. 1956 Official Language: Punjabi
Rajasthan
- Rajasthan covers an area of 342,239 square kilometers (132,139 sq mi) or 10.4 percent of the total geographical area of India.
- It is the largest Indian state by area and the seventh-largest by population.
- Rajasthan is located on the northwestern side of India, where it comprises most of the wide and inhospitable Thar Desert.
- It is bordered by five other Indian states: Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, and Gujarat. The Tropic of Cancer passes through the southernmost tip of the state.
Capital: Jaipur Founded on: 1 Nov. 1956 Official Language: Hindi
Sikkim
- Sikkim is a state in northeastern India and it is the least populous and second smallest among the Indian states.
- A part of the Eastern Himalaya, Sikkim is notable for its biodiversity, including alpine and subtropical climates, as well as being a host to Kangchenjunga, the highest peak in India and third highest on Earth. Sikkim’s capital and largest city is Gangtok.
- Almost 35% of the state is covered by the Khangchendzonga National Park which is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Sikkim’s economy is largely dependent on agriculture and tourism.
Capital: Gangtok Founded on: 16 May. 1975 Official Language: English, Nepali, Sikkimese, Lepcha
Tamil Nadu
- Tamil Nadu lies in the southernmost part of the Indian subcontinent and is bordered by the union territory of Puducherry and the South Indian states of Kerala, Karnataka, and Andhra Pradesh.
- It is bounded by the Eastern Ghats on the north, by the Nilgiri Mountains, the Meghamalai Hills, and Kerala on the west, by the Bay of Bengal in the east, by the Gulf of Mannar and the Palk Strait on the southeast, and by the Indian Ocean on the south.
- The state shares a maritime border with the nation of Sri Lanka.
Capital: Chennai Founded on: 26 Jan. 1950 Official Language: Tamil
Tripura
- Tripura is a state on the northeastern side of India. The third-smallest state in the country, it covers 10,491.69 km2.
- According to the 2011 census, the state had 3,671,032 residents, constituting 0.3% of the country’s population.
- Forests cover more than half of the area, in which bamboo and cane tracts are common. Tripura has the highest number of primate species found in any Indian state.
Capital: Agartala Founded on: 21 Jan. 1972 Official Language: Bengali, English, Kokborok
Telangana
- Telangana is a state in Southern India situated on the south-central stretch of the Indian peninsula on the high Deccan Plateau.
- It is the eleventh-largest state and the twelfth most populated state in India with a geographical area of 112,077 km2 and 35,193,978 residents as per the 2011 census.
- Telangana is bordered by the states of Maharashtra to the north, Chhattisgarh to the east, Karnataka to the west, and Andhra Pradesh to the east and south.
Capital: Hyderabad Founded on: 2 Jun. 2014 Official Language: Telugu
Uttar Pradesh
- With over 200 million inhabitants, Uttar Pradesh is the most populous state in India as well as the most populous country subdivision in the world.
- The state is divided into 18 divisions and 75 districts, with the state capital being Lucknow, and Allahabad serving as the judicial capital.
- The forest cover in the state is 6.1% of the state’s geographical area. The state is bordered by Rajasthan, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Delhi, Uttarakhand, Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, and an international border with Nepal.
Capital: Lucknow Founded on: 26 Jan. 1950 Official Language: Hindi
Uttarakhand
- Uttarakhand is a state in the northern part of India. Uttarakhand is known for the natural environment of the Himalayas, the Bhabar, and the Terai regions.
- It shares international borders with China and Nepal whereas it shares borders with the Indian states Uttar Pradesh and Himachal Pradesh.
- According to the 2011 Census of India, Uttarakhand has a population of 10,086,292, making it the 20th most populous state in India.
Capital: Dehradun Founded on: 9 Nov. 2000 Official Language: Hindi
West Bengal
- West Bengal is a state in the eastern region of India along the Bay of Bengal.
- With over 91 million inhabitants, it is the fourth-most populous state and the fourteenth-largest state by area in India. Covering an area of 88,752 km2, it is also the eighth-most populous country subdivision of the world.
- It shares its borders with Bangladesh in the east and Nepal and Bhutan in the north. It also borders the Indian states of Odisha, Jharkhand, Bihar, Sikkim, and Assam.
Capital: Kolkata Founded on: 1 Nov. 1956 Official Language: English, Bengali